If you are just starting out with Web3 development, it can be very intimidating at first.
Web3 is growing rapidly and new vocabularies are springing up every day. There are plenty of words to learn so we’ve curated the top Web3 terminologies that will bring you up to speed and make you sound like a pro even if you are a total newcomer.
1. Web 1.0
This is often used to describe the earliest version of the internet which had its origin in the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA).
Unlike what we have today, Web 1.0 web pages were built using only simple HTML codes and consisted of static pages. It is also referred to as the read-only web because most of the interactions were one way. That is, readers can only read the content without participating through comments or sharing of the pages.

2. Web 2.0
This is the direct successor of Web 1.0 and the internet as we know it today. The shift from Web 1.0 to Web 2.0 is marked by an increase in users generating content and actively interacting with the internet.
This is the era where social media platforms became increasingly popular and users can share content in the form of ideas, text, pictures, or videos.
3. Web 3.0
In this era of Web 2.0, the internet is dominated by a few tech giants such as Facebook, Google, and Amazon who have access to and control user data.
Web 3.0 describes the idea of the next generation of the internet where the information shared on the web is decentralized. You can think of it as an internet owned by everyone (both the builders and users).
Although Web 3.0 is still in its infancy stage, the possibilities are limitless. Once it is fully in place, tech giants like Facebook will no longer be able to control or access user data.
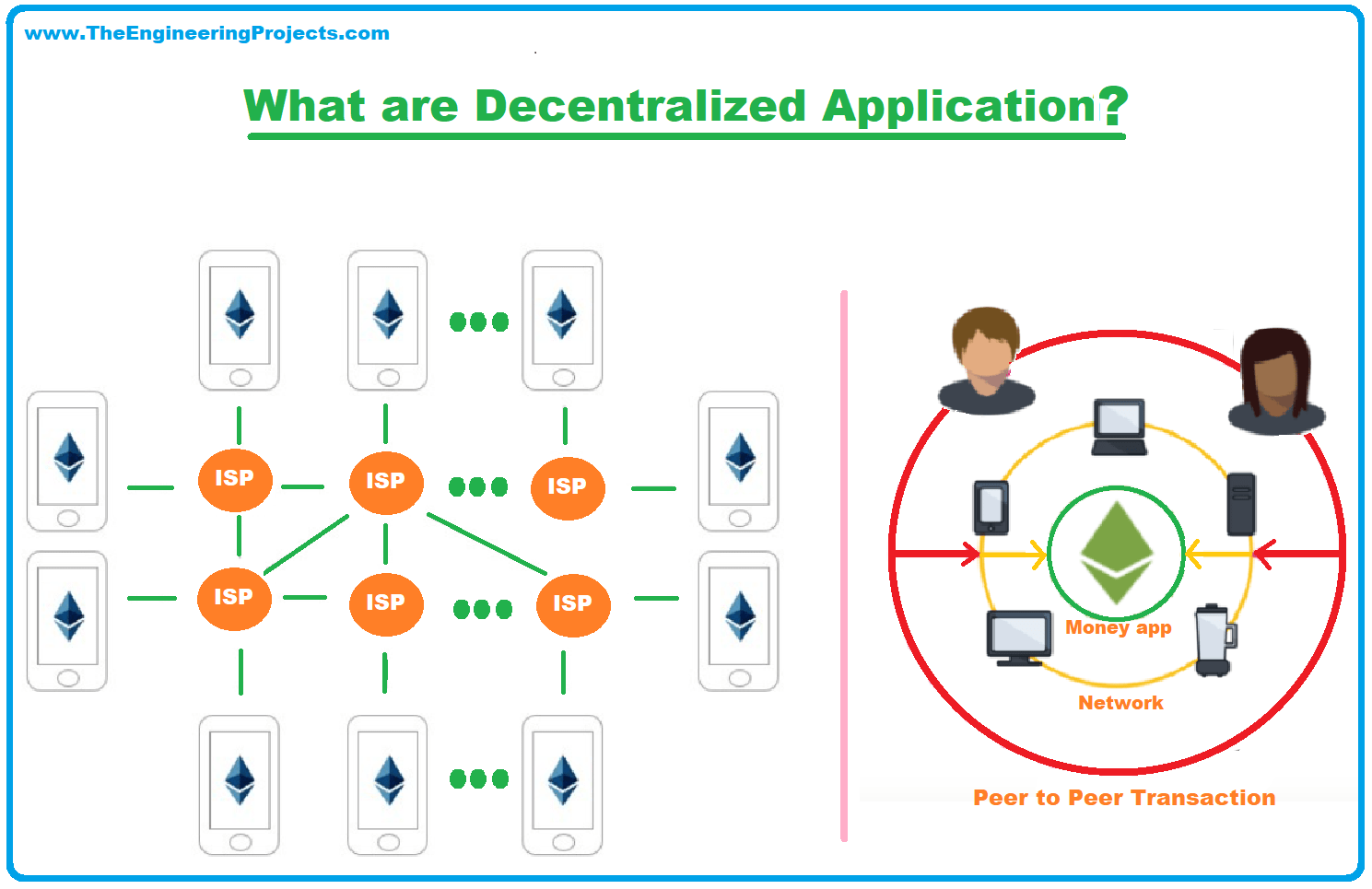
4. Decentralized Applications (dApps)
Just as the name implies, decentralized applications are applications that run on a decentralized network. Unlike traditional applications, dApps are distributed on a network of computer nodes and they are not controlled by a single person.
DApps are controlled using smart contracts and tokens are distributed to users to represent ownership. Some popular examples of decentralized applications include Augur, Uniswap, and CryproKitties.
This technology has many practical applications in fields such as finance, security, media, social, and health among others.
5. Decentralized Finance (Defi)
Another important Web3 terminology that is generating buzz these days is decentralized finance or Defi. This is a movement encouraging alternatives to traditional forms of banking using blockchain technology.
For instance, in traditional banking, getting access to loans requires several paper works and a good credit score. However, with decentralized finance, almost anyone can get access to financing instantly.
Decentralized finance also makes use of smart contracts to eliminate the need for a central agency such as the central banks or government.
6. Smart Contracts
We’ve talked about smart contracts in dApps and Defi but what exactly are they? To understand smart contracts, think about the processes that every transaction has to go through in banks before it is approved.
What if these processes can be performed automatically once certain conditions are met? This is where smart contracts come in.
A smart contract is a self-executing computer protocol intended to facilitate, verify and enforce the terms of agreement of a contract on the blockchain network.
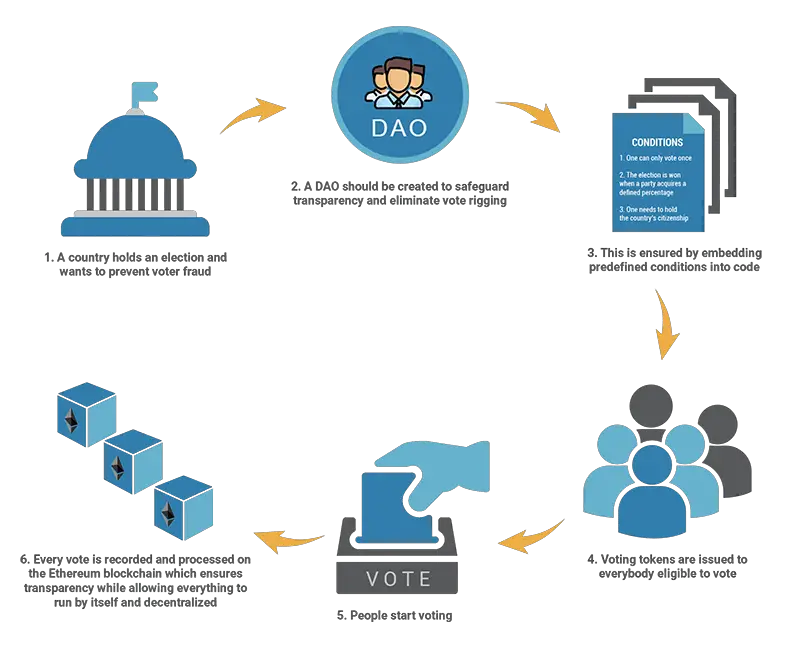
7. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
Simply put, a DAO is an organization built on blockchain technology and governed in a decentralized manner through smart contracts.
The main idea behind DAOs is to build an organization with mutual goals where decisions can be made by all members. To do this, DAO organizations issue crypto tokens to community members. All financial operations performed by such companies are recorded on the blockchain making them completely transparent.
8. Non-Fungible Token
Non-fungible tokens, also known as NFTs, have grown in popularity in recent years. All thanks to the hypes from celebrities such as Snoop Dogg and big companies such as Nike who have invested in them. However, the idea that most people have about NFTs is not accurate.
NFTs are a unique asset class that cannot be exchanged with one another. One easy way to understand NFTs is to think of a famous painting such as the Mona Lisa painting by Leonardo da Vinci.
Although you could snap the painting and reproduce an identical copy, the original painting would still have more value. NFTs are just like the Mona Lisa painting but in digital format on the blockchain network. Each NFT is unique and traceable and because of their rarity, they are also valuable.
9. ERC 721
Ethereum is the most established blockchain for NFTs and this is only possible because of the ERC 721. The ERC 721 refers to a token standard for non-fungible tokens.
With the introduction of this standard, it became possible to add unique codes to a digital asset that will make it traceable. The CryptoKitties were perhaps the asset class that made this standard became famous.
10. ERC 20
Before the ERC 720, there was the ERC 20 token standard which allows fungible tokens to be built on the Ethereum blockchain. These assets became popular in 2017 and 2018 during the boom in initial coin offerings.
Although many of them are now irrelevant, some popular digital currencies use the ERC 20 standard such as Maker (MKR), Basic Attention Token (BAT), and Augur (REP).
11. Ethereum 2.0
Ethereum 2.0, also known as ETH 2.0, is a major upgrade to the Ethereum network currently underway. This upgrade will result in the Ethereum blockchain shifting from a proof-of-work consensus (which consumes more energy) to a proof-of-stake.
One of the major reasons for this upgrade is to make transactions performed on the Ethereum network faster. In addition to this, moving to proof-of-stake will reduce the energy consumption of Ethereum transactions by up to 99 per cent.

12. Genesis Block
This refers to the first “block” of a blockchain that does not reference a previous block. A blockchain usually has multiple “blocks” where every transaction is recorded.
Each block contains information from the previous block but the genesis block is the first block often referred to as block 0 or block 1.
13. Metaverse
The metaverse is another web3 technology that is fast gaining popularity among many people today. It explains a concept of a digital universe that contains all the aspects of the real world.
While this concept is still very new, there is a rush to participate in this digital real estate even among big tech companies.
In the future, the metaverse and Web 3.0 would support each other perfectly. While Web 3.0 would provide a user-focused internet, the metaverse is how you will experience it.

Aaron Boluwatife is a freelance content writer and SEO copywriter for Fintech, SaaS and Cryptocurrency websites. He helps businesses generate more traffic and sales through his knowledge of SEO and Copywriting,
